Record-Breaking Lungfish Genome Reveals Secrets of Early Land Vertebrates
21 Aug 2024
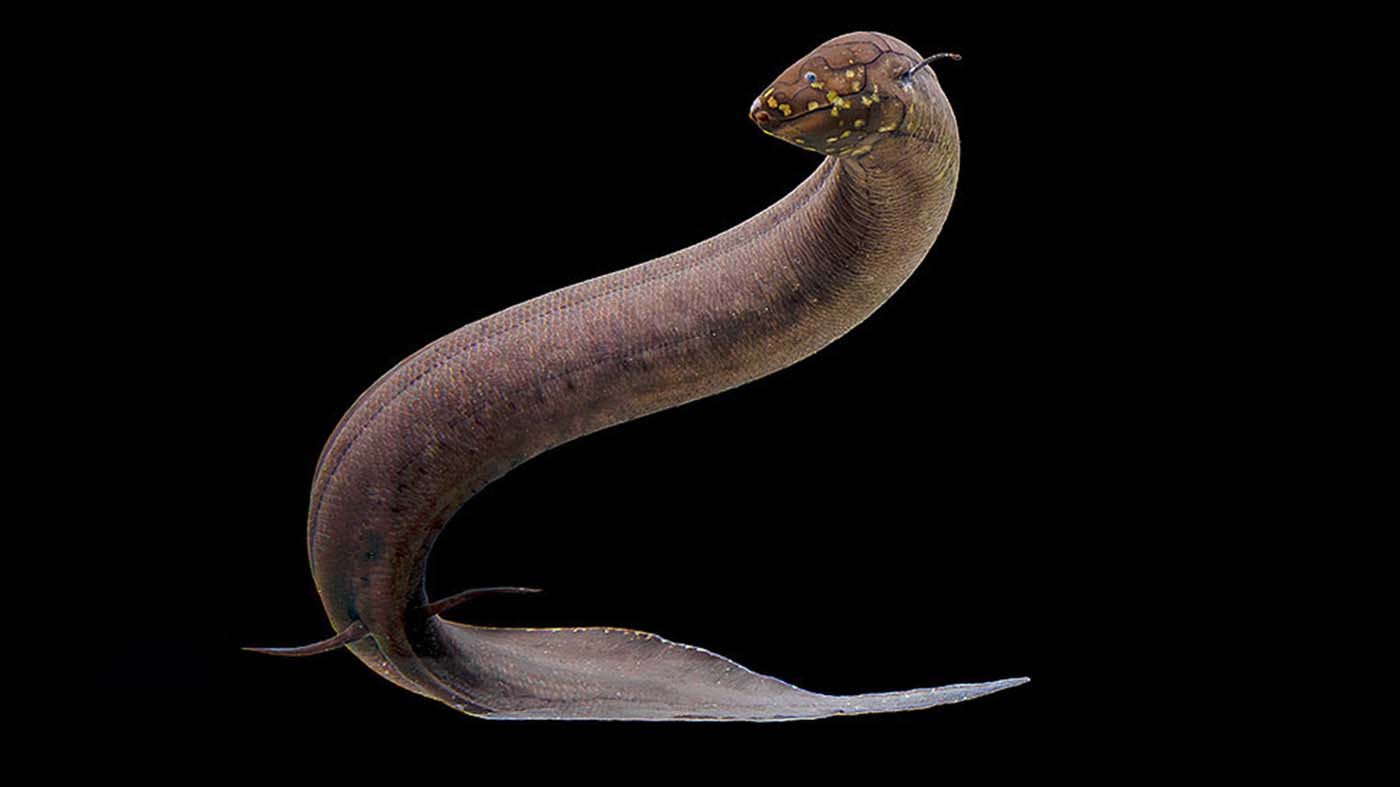
Scientists have sequenced the largest animal genome, belonging to the South American lungfish. At 90 billion base pairs, it's 30 times larger than the human genome, offering insights into early vertebrate evolution and the transition to life on land.